Are you interested in the world of cryptocurrencies and want to learn more about Bitcoin halving? The next Bitcoin halving date is scheduled to occur in around May the year 2024, approximately four years after the previous halving which occurred in 2020.
In this blog post, we will delve into the specifics of the halving event, including when it is expected to occur and its implications for the cryptocurrency market. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or new to the world of Bitcoin, this blog post will provide you with a detailed analysis of the Bitcoin halving event and what it means for the future of the cryptocurrencies.
Read on and learn everything you need to know about Bitcoin Halving!
Table of Contents:
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is a significant event in the world of cryptocurrencies. It refers to the pre-programmed process of reducing the reward for mining new Bitcoins by half approximately every four years. This feature is built into the Bitcoin protocol and is aimed at regulating the supply of Bitcoin and ensuring that it becomes scarcer over time.
As you may already know, the maximum number of Bitcoins that will ever be created is 21 million. Bitcoin halving is an essential step towards achieving this goal. By halving the reward for mining, the rate at which new Bitcoins are created slows down, which helps to preserve its value over time.
In addition, Bitcoin halving is also a crucial event in the Bitcoin ecosystem when it plays a significant role in regulating the supply of Bitcoin and its value. As we have seen in the past, Bitcoin halving can lead to a rise in the price of Bitcoin due to the reduced supply. Therefore, it is important for investors and traders to stay informed about Bitcoin halving and its effects.
Important Takeaways
- Bitcoin halving can lead to increased competition among miners.
- The effect of Bitcoin halving on the price of Bitcoin is not immediate: in some cases, it can take several months or even years for the effects of halving to be felt.
- The last Bitcoin will not be mined until the year 2140. At that point: all 21 million Bitcoins will have been mined, and the supply of Bitcoin will be fixed.
- Bitcoin halving can affect the entire cryptocurrency market: inlcluding transaction and other crypto coins.
Bitcoin Havling History
Bitcoin was created in 2009, and at that time, miners received 50 BTC for each block they mined. In 2012, the reward was halved to 25 BTC, and four years later, it was halved again to 12.5 BTC. The next halving date is expected to occur in 2024, which will reduce the reward to 6.25 BTC.
| Reward per Block | Number of Blocks | Bitcoin Price on Halving Day | New Bitcoin Generated | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Launch of Bitcoin | 50 BTC | 0 | 0 (original price) | 10,500,000 BTC |
| 1st Halving | 25 BTC | 210,000 | $12.35 | 5,250,000 BTC |
| 2nd Halving | 12.5 BTC | 420,000 | $650.53 | 2,625,000 BTC |
| 3rd Halving | 6.25 BTC | 630,000 | $8,821.42 | 1,312,500 BTC |
| 4th Halving Expected | 3.125 BTC | 740,000 | Unknown | 656,250 BTC |
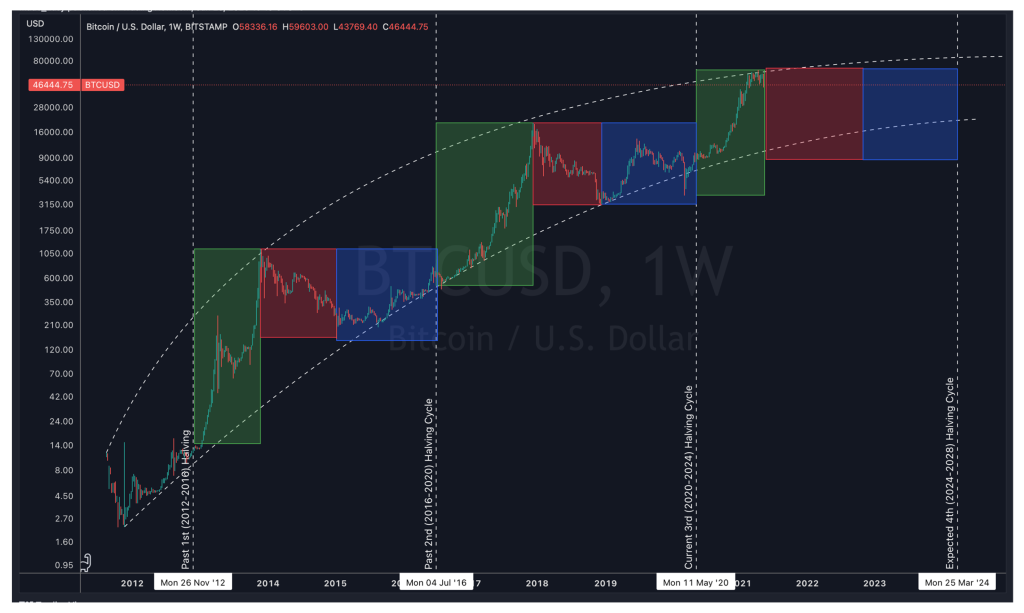
The Cycle of Bitcoin Halvings. Figure 1 shows a weekly candlestick chart of the Bitcoin price in log-scale, highlighting the three phases that typically occur during each cycle: a bull market (represented by the green box), a bear market (represented by the red box), and a recovery phase (represented by the blue box). Each halving cycle is marked by a vertical line indicating the start of the respective week. The first halving cycle took place on November 28, 2012, the second on July 9, 2016, and the third on May 11, 2020. It’s important to note that Figure 1 depicts a weekly chart.
When is the Next Bitcoin Halving?
The next Bitcoin halving is scheduled to occur in the year 2024, approximately four years after the previous halving which occurred in 2020. However, the exact date of the next halving is not fixed because the halving is triggered by the creation of a certain number of new Bitcoin blocks, which can vary in terms of the time it takes to create them. Based on the current rate of block creation, the next Bitcoin halving is expected to take place around May 2024.
What’s the Effects of Bitcoin Havling?
Inceasing Transaction fees
The cost of transaction fees tends to increase after halving events. This is due to the decreased block reward that miners receive, which can lead to an increase in the competition among miners to validate transactions. Consequently, higher transaction fees are required to incentivize miners to include transactions in their blocks. Consequently, higher transaction fees are required to incentivize miners to include transactions in their blocks.
Increasing Mining Difficulty
Bitcoin halving has a significant impact on mining difficulty, which refers to the amount of computational power required to mine a block on the blockchain. As the mining reward decreases, the competition among miners increases, leading to a rise in mining difficulty. This can make mining less profitable for small-scale miners, who may exit the market, leaving only the more significant mining pools.
Decreasing in Mining Profitability
Another effect of Bitcoin halving is that it can make mining less profitable for miners. When the reward for mining is cut in half, miners receive fewer Bitcoins for their work, which can make it harder to cover the cost of equipment, electricity, and other expenses. Some miners may decide to shut down their operations or switch to mining other cryptocurrencies that are more profitable.
Rising in Bitcoin Price
The price of Bitcoin has historically been heavily influenced by halving events. The reduction in the mining reward reduces the rate at which new Bitcoin is added to the supply, making it more scarce and valuable. This reduction in supply, combined with an increase in demand, can lead to an increase in the price of Bitcoin.
However, the price of Bitcoin does not always increase after halving events. In some cases, there may be a short-term decrease in price due to market fluctuations or speculation. Nonetheless, the long-term effects of halving on the price of Bitcoin have been largely positive, with each halving event resulting in a significant increase in price. This makes Bitcoin an attractive investment for investors who are looking for a store of value or a hedge against inflation.
Learn more about bitcoin halving effects:
Why Bitcoin Havling Occur?
Bitcoin’s key ideas include, as previously discussed, independence from intermediaries and regulators, as well as the autonomy of the network functioning. However, Bitcoin’s intent, according to its creator (or creators), was to eliminate the chief disadvantage of modern money equivalents – inflation. The idea of a perfect money, which in the long run does not lose its value, was fully realized in this cryptocurrency and significantly contributed to its success. Therefore, to prevent inflation, the code of cryptocurrency originally had several basic regulating principles:
- Limited issuance;
- Increase/decrease in the complexity of mining;
- Halving of the reward for the generated block.
These principles are implemented through the process of Bitcoin halving, which is an integral part of the Bitcoin protocol. Bitcoin halving is a process in which the reward for mining new Bitcoins is reduced by half approximately every four years. The maximum number of Bitcoins that will ever be created is 21 million. By halving the reward for mining the rate at which new Bitcoins are created slows down, helping to preserve its value over time.
Other Cryptocurrencies and Halving
Bitcoin is not the only cryptocurrency that uses halving as a mechanism to control the supply of new coins. Several other cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin and Bitcoin Cash, also use halving as a way to maintain scarcity.
Litecoin, for example, has a block reward of 12.5 LTC per block, with halving occurring approximately every four years. The most recent Litecoin halving took place in August 2019, reducing the block reward to 12.5 LTC per block.
Bitcoin Cash, a fork of Bitcoin, also uses halving to control the supply of new coins. Bitcoin Cash has a block reward of 6.25 BCH per block, with halving occurring approximately every four years. The most recent Bitcoin Cash halving took place in April 2020, reducing the block reward to 6.25 BCH per block.
FAQ
1.How can I prepare for Bitcoin halving as an investor or trader?
Investors and traders should stay informed about the latest news and developments related to Bitcoin halving. They can monitor the Bitcoin price and trading volumes leading up to and after the halving event to identify any patterns or trends. It is also a good idea to diversify your cryptocurrency portfolio to minimize the risks associated with any one cryptocurrency.
2.What happens after all 21 million Bitcoins are mined?
After all 21 million Bitcoins are mined, miners will no longer receive block rewards. Instead, they will only receive transaction fees as a reward for verifying transactions. This could lead to increased competition among miners for transaction fees, and could also incentivize users to hold onto their Bitcoins rather than spending them.
3.Will there ever be more than 21 million Bitcoins?
No, there will never be more than 21 million Bitcoins. The maximum supply of Bitcoin is fixed at 21 million, and once this number is reached, no new Bitcoins will be created. This is built into the Bitcoin protocol as a way to control inflation and ensure that the value of Bitcoin is preserved over time.
4. What is the impact of Bitcoin halving on the overall cryptocurrency market?
Bitcoin is the largest and most influential cryptocurrency, so any significant event in the Bitcoin ecosystem can affect the entire market. Bitcoin halving can lead to increased demand for Bitcoin, as the reduced supply can drive up the price. At the same time, it can also make mining less profitable, which may cause some miners to switch to other cryptocurrencies or drop out of the market altogether.